Cisco IOS (Internetwork Operating System) is a crucial component of Cisco devices, responsible for network functionality, management, and security. Regularly updating IOS can enhance network performance, fix vulnerabilities, add new features, and improve stability.
Before delving into how to upgrade Cisco IOS, it's important to recognize that Cisco IOS supports both upgrades and downgrades. This flexibility means administrators can install a higher version for enhanced features or revert to a stable version if issues arise. It is recommended to check release notes and compatibility issues before proceeding with an upgrade or downgrade to ensure a smooth process.
Developed in the 1980s by Stanford University engineer William Yeager, Cisco IOS serves as the brain of Cisco networking devices, controlling operations and enabling communication and network management. Its core functions include interface configuration, Quality of Service (QoS), network management and monitoring, as well as security features for routers, switches, and more. Additionally, it offers a range of additional services such as authentication, firewall capabilities, encryption, deep packet inspection, policy enforcement, and intelligent routing, enhancing network traffic security and performance.
To address the limitations of traditional Cisco IOS and adapt to emerging network demands, Cisco introduced Cisco IOS XE, a comprehensively restructured and expanded version based on the legacy IOS.
Cisco IOS operates on a monolithic operating system, running all modules within the same memory space without memory separation. This means that if a process or module crashes, the entire system becomes unresponsive. Upgrading the system requires upgrading the entire IOS, causing a system-wide interruption.
In contrast, Cisco IOS-XE operates on a Linux kernel with monolithic applications running on top, representing an upgrade to the traditional IOS. It retains the same visual appearance as Cisco IOS while offering enhanced future-proofing and improved functionalities. For example, IOSd in the Cisco IOS XE environment supports multi-core CPUs and multithreading, and Cisco IOS XE offers management and support without the need for retraining from traditional IOS.
Unlike Cisco IOS, in IOS-XE, IOS runs as a daemon on top of the Linux kernel, with various functions implemented as separate processes (sub-packages). This new modular design allows each sub-package to be independent, enabling the upgrade of individual components without affecting the entire system. If a component fails, this design can confine the failure to a specific part of the system.
Cisco IOS XE represents a significant evolution of Cisco IOS, indicating a new direction in the development of network operating systems. By introducing a modern operating system architecture, supporting multithreading, and enhancing security and functionality, IOS XE provides higher performance, scalability, and flexibility for Cisco devices. As network demands continue to evolve, Cisco IOS XE will continue to play a key role in driving innovation and development for enterprises and service providers.
Regularly upgrading Cisco IOS is essential for ensuring the security, performance, and functionality of network devices. Here is a guide for upgrading Cisco IOS on routers, specifically the C3650 series, as an example:
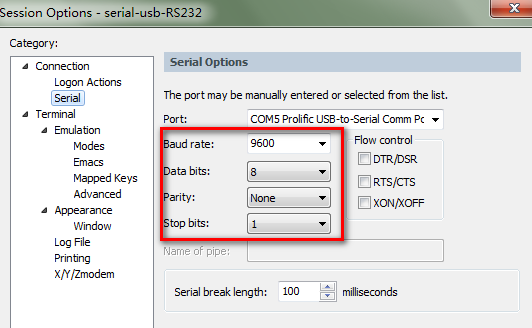
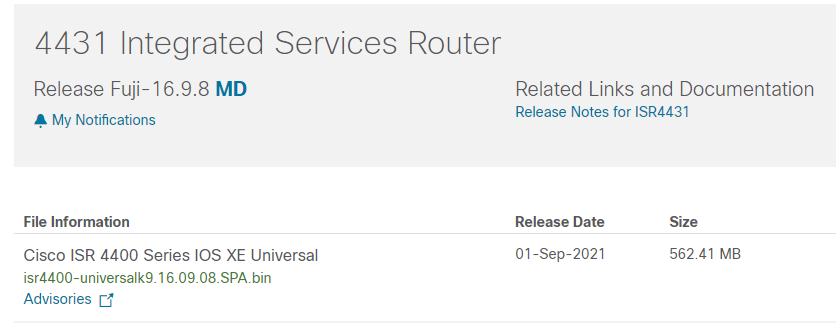
Router# copy tftp://10.1.1.1/***.bin flash:***.binRouter# dir flash:.Router(config) boot system bootflash:***.bin.Router # write memory and Router # reload.show version command to verify the Cisco IOS software.The role of Cisco IOS in Cisco switches and routers is vital, providing not only basic network connectivity but also a wealth of security, management, and protocol support functions. Regularly upgrading Cisco IOS is a key measure to ensure network security, functionality, and stable operation, helping network administrators ensure a modern and effectively managed network environment.